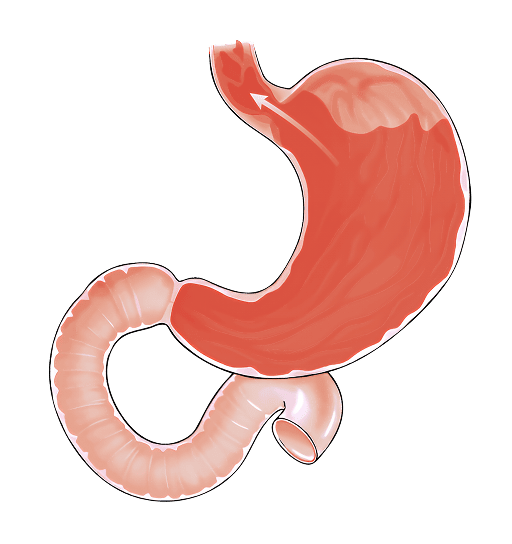
With 2 clinics located in Central London and 2 in North-West London, Dr Arun Rajendran takes pride in offering expert, friendly, and effective care for a comprehensive range of conditions affecting the gullet, stomach, colon, and liver.
+44 (0)20 3404 5254
mailgastro@pm.me
London clinic and Onewelbeck
BMI The Clementine Churchill Hospital
OSD Healthcare